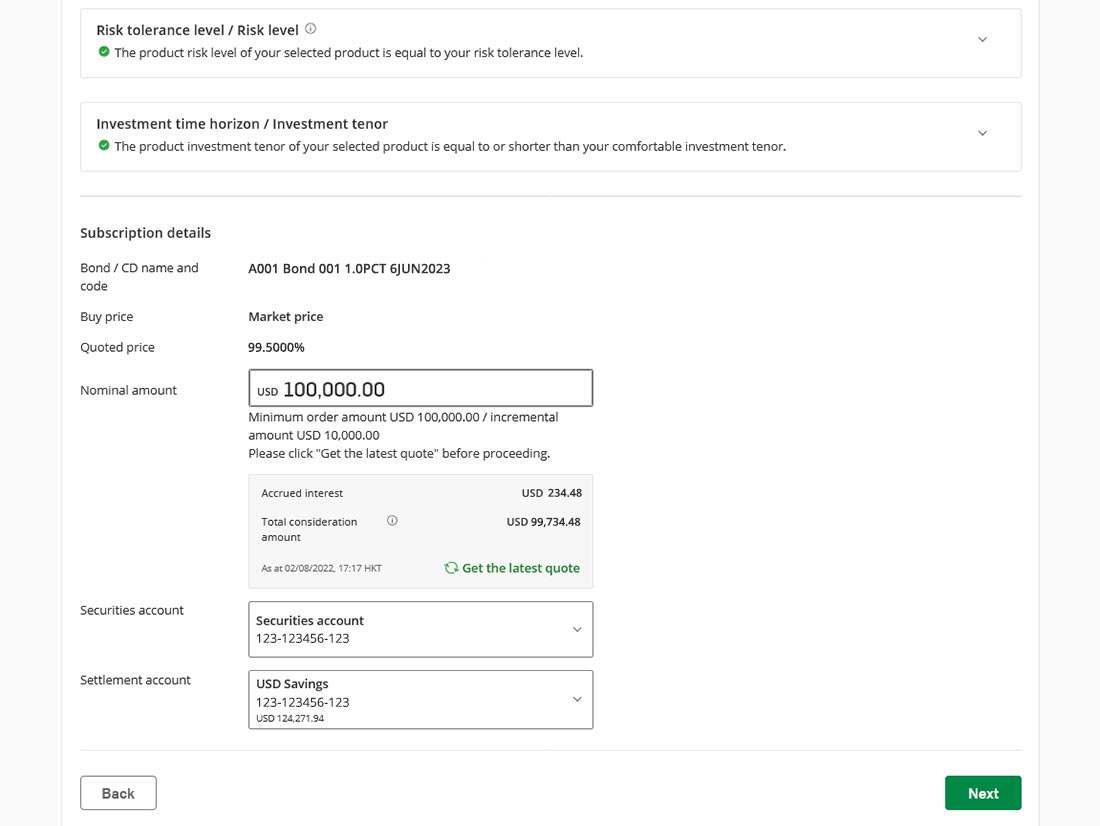
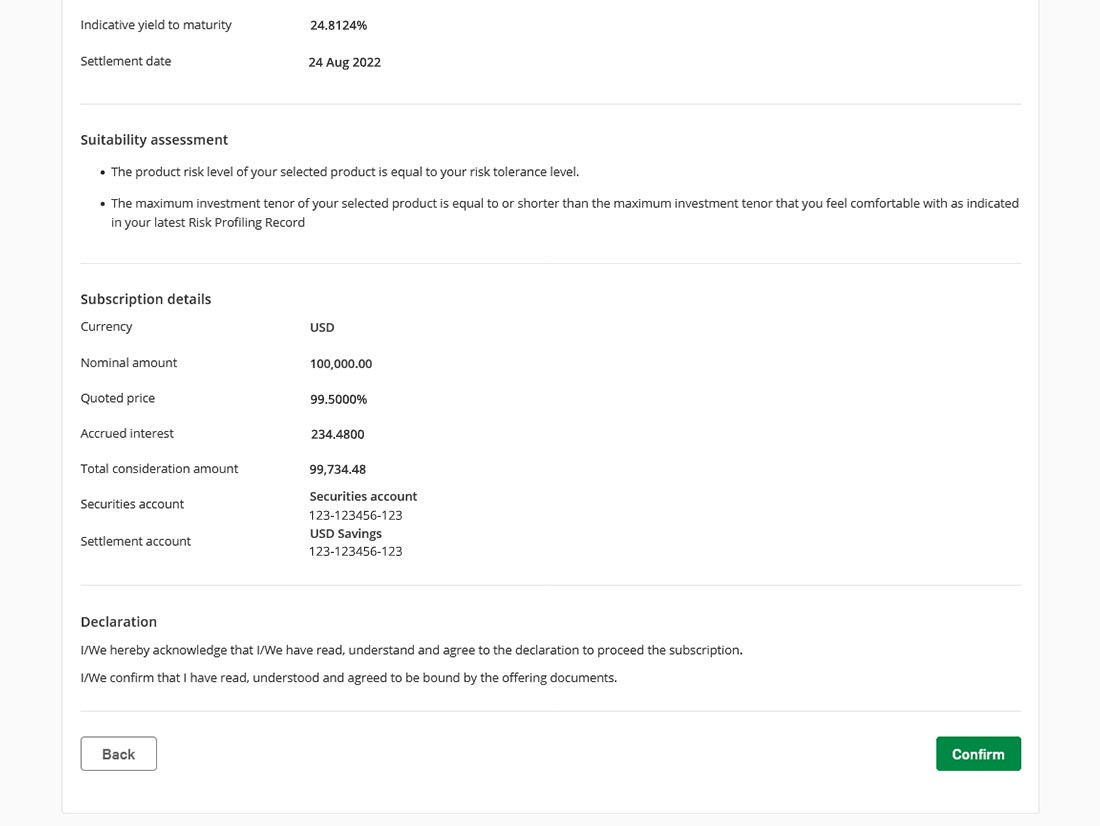
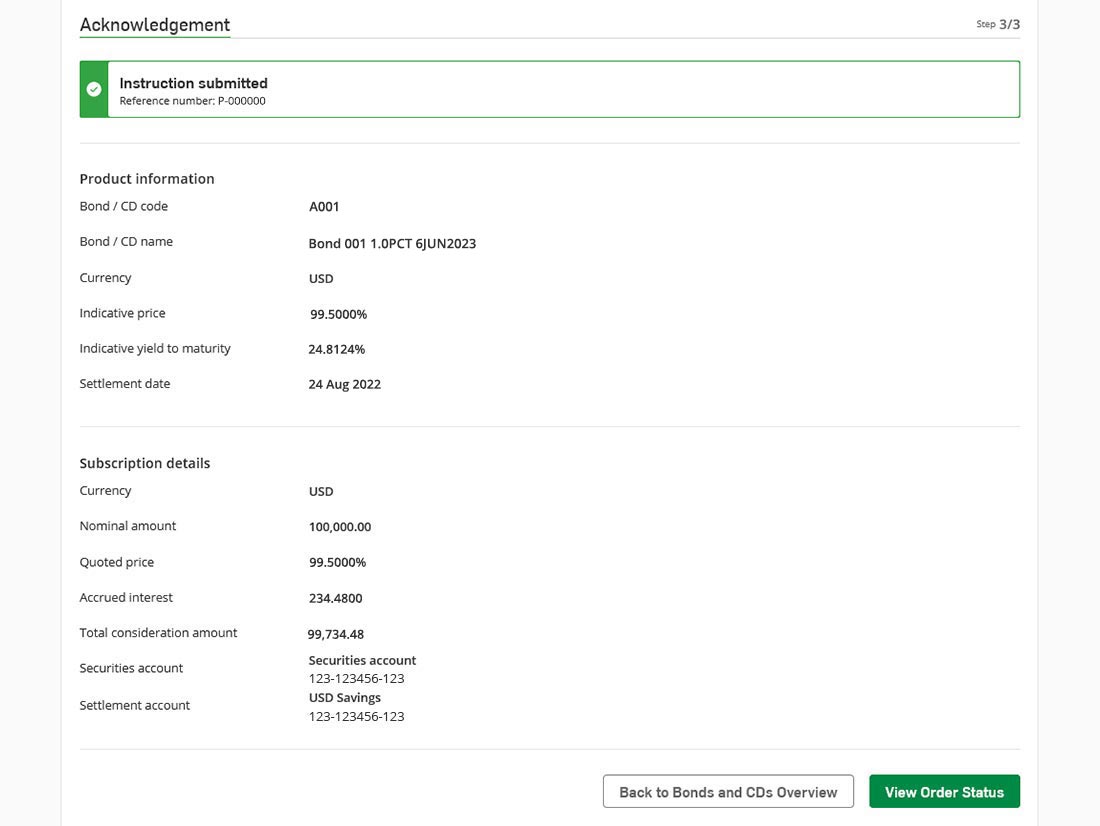
We use cookies to give you the best possible experience on our website. By continuing to browse this site, you give consent for cookies to be used. For more details, please read our Online Terms & Conditions, Privacy Policy, Cookies Policy and Personal Information Collection Statement.
Menu
- Banking
- Investments
- Cards
- Loans
- Mortgages
- Insurance & MPF
- Life Protection eCancerPro Insurance Plan (Apply online)eFamilyPro Life Insurance Plan (Apply online)EmbraceLife Insurance PlanCompanionLife Insurance PlanExquisite Universal Life Insurance SeriesSplendid Universal Life Insurance PlanMortgage Life Protection PlanPhoenixLife Insurance PlanHang Seng OliveInsurance ExplorerView all Life Protection
- Retirement / Wealth Accumulation eIncomePro Deferred Annuity Plan (100% Guaranteed) (Apply online)QuickReward Endowment Life Insurance Plan (1-Year) (Apply online)5-Year eEndowment Life Insurance Plan (Apply online)CouponPower Guaranteed Life Insurance Plan (Apply online)FortuneLife Deferred Annuity Life Insurance PlanDragonPower Life Insurance PlanPhoenixPower Life Insurance PlanIncomePower Life Insurance PlanLegendPower Life Insurance PlanFamilyPower Multi-Currency Insurance PlanInsurance ExplorerView all Retirement / Wealth Accumulation
- Medical & Critical Illness
- Travel & Overseas Study
- Household & Others
- MPF / ORSO
- View All Insurance & MPF
- Life Protection
- Offers
Log on using mobile browser
We recommend using a computer web browser or Hang Seng Mobile App to log on for enhanced security. Please visit "Security Information Centre" for more security tips.